
STRUCTURE
|
WRC About center
|
|
|
|
|
Theoretical and experimental investigations of structure and kinetics of associate fluid media and solutions are carried out in the laboratory. New optical and ultrasonic research techniques for such media are developed.
Staff
The Laboratory is headed by N. V. Suyazov, Ph.D.
PRINCIPAL FIELDS OF RESEARCH
BASIC EQUIPMENT
Fig.1
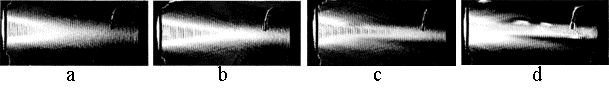
Dynamics of self-action of an ultrasonic beam in a viscous liquid (in glycerin) is shown in Fig. 1. Intensity distribution of sound field at (à) 0,1 s, (b) 5 s, (c) 10 s, and (d) 15 s intervals after initialization of a sonic source (the power is 8 W).
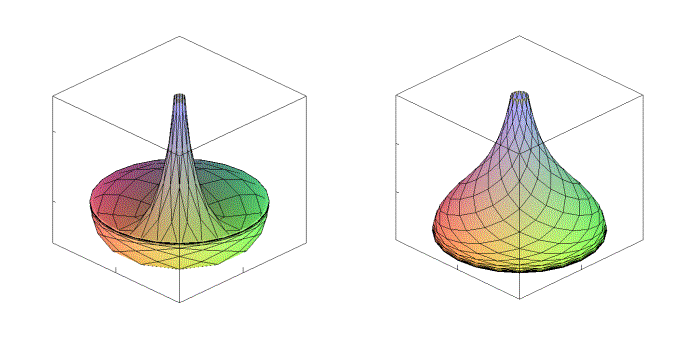
Fig.2
MOST IMPORTANT RESULTS
- Mechanism of phase transitions induced by parametric noise are proposed and described for media with intermolecular hydrogen bonds; the developed model is applicable to both thermodynamics and nonlinear dynamics of determined systems of general form and to population dynamics;
- A group subordination model describing the symmetry of phase states and phase diagram topology is designed for water;
- ·A physical mechanism connecting the parameters of the Raman spectrum of water with entropy and concentration of H-bonds is found out; the temperature anomalies of the spectrum have been identified with phase transitions in a network of H-bonds;
- A physical model controlled by new sine-Gordon-type equations is developed; it is demonstrated that the surfaces generated by these equations realize the transition from the sphere geometry to the Beltrami pseudosphere geometry (Fig. 2).
- New methods for remote ultrasonic diagnostics of physical media, structures and formations are proposed and implemented experimentally.
|
|
|
|